abstract—a
brief summary of an article's content. Abstracts can save you time by
helping you identify the best articles on your topic.
browsers—provide a graphical interface to information on the Web. They display pages written in HTML and make it possible for you to click on links to jump to other pages. This neat invention is called hypertext.
The most popular browsers are Netscape's Navigator/Communicator and Microsoft's Internet Explorer. Regardless of which browser you choose, you can access the same information and can configure the software to match your personal preferences.
Each browser
interprets some HTML elements in its own way, so the same page might display
differently, depending on whuch brower you use.
Some types of databases are:
Print
Databases
The index of a book is a print database. It allows you to go quickly to
a topic in the book. A phone book is another type of print database.
Electronic Databases
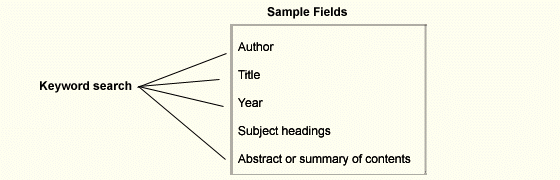
We usually think of searchable electronic indexes and catalogs when we
refer to databases. ProQuest Direct is an example of an electronic
database. It quickly looks for a topic in periodicals.

full
text—the
complete text of an article available online. Some periodical databases
provide full text articles. If the full text is available, you'll see
this symbol next to the citation: ![]()
B - Philosophy
C - Auxiliary sciences of history
D - History (general)
E-F - History (Americas)
G - Geography
H - Social sciences
J - Political science
K - Law
L - Education
N - Visual arts
P - Language and literature
Q - Science
R - Medicine
S - Agriculture
T - Technology
U - Military science
V - Naval science
Z - Bibliography; library science
Each branch is divided into more specific topics represented by combinations of letters and numbers. For example, the book Teleworking has the call number HD 2336.3 B523 1995:
H
- Social sciences and business
HD - Economic history and conditions
2321 - 4730 - Industry
2331 - 2336 - Household Industry
2336.3 - Telecommuting